Estate Planning
Nov 29, 2024
7 Critical Trust Fund Mistakes Parents Must Avoid in 2025
Setting up a trust fund? Learn the biggest mistake parents make and ensure your child's financial security with expert guidance.
Explore how family trusts can reduce tax liabilities and possibly defer probate, offering a secure future for your loved ones. Find out how to set one up in Canada.


If you’ve dedicated a lifetime to building an asset base and caring for your family, establishing a family trust might be the next essential step in continuing that legacy. The family trust not only helps reduce tax liability, protects assets, increases privacy, but also helps your estate avoid probate when you pass away.
The following sections will explain everything you need to know about family trust in Canada, including the different types, their benefits, tax implications, and the steps to establish one.
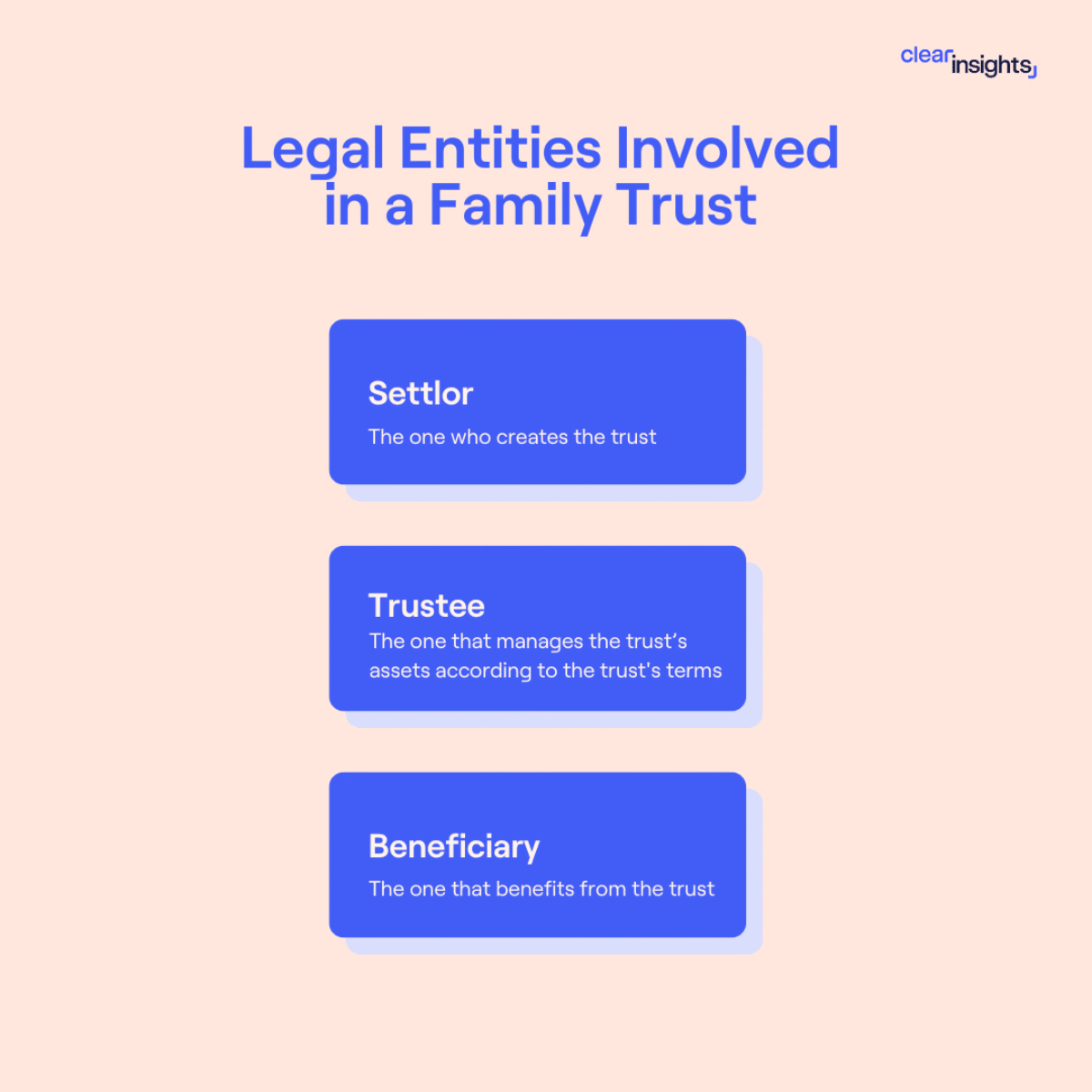
A family trust is a legal arrangement where a settlor transfers assets—such as money, real estate, or investments—to a trustee, who manages them for the benefit of designated beneficiaries. This structure allows for asset protection, tax planning, and controlled wealth distribution, both during the settlor’s lifetime and after their passing.
The trust agreement outlines key details, including:
The trustee’s powers and responsibilities
The named beneficiaries (e.g., children, spouses, corporations)
How assets are managed and distributed
In Canada, the trustees can be parents, grandparents, or other older family members. These are the people whose role and duty will be to manage the trust. The beneficiaries you can include in a family trust are children, spouses, grandchildren, parents, charitable organizations, or corporations.
A family trust serves as a strategic estate planning tool, allowing you to manage your finances efficiently during your lifetime and after your passing.T hey promote asset protection by holding the property on behalf of your beneficiaries. They also ensure your property passes on to the beneficiaries without going to court, thus avoiding the lengthy, and costly probate process.
A family trust helps with wealth management and financial planning for your trustees. As you create the trust, you can outline how you want the assets to be used and managed to ensure continuity and wealth preservation for future generations. You can outline when and how minors can access the funds and what to do with the money. Your trustee should have an idea of wealth management to ensure proper asset utilization.
Establishing a family trust in Canada is straightforward if you understand the key requirements and seek legal advice to ensure its validity. To be legally binding, a trust agreement must meet specific conditions:
For a trust to be legally binding, the trustor must clearly express intent, own the assets being transferred, and specify the beneficiaries and their entitlements.
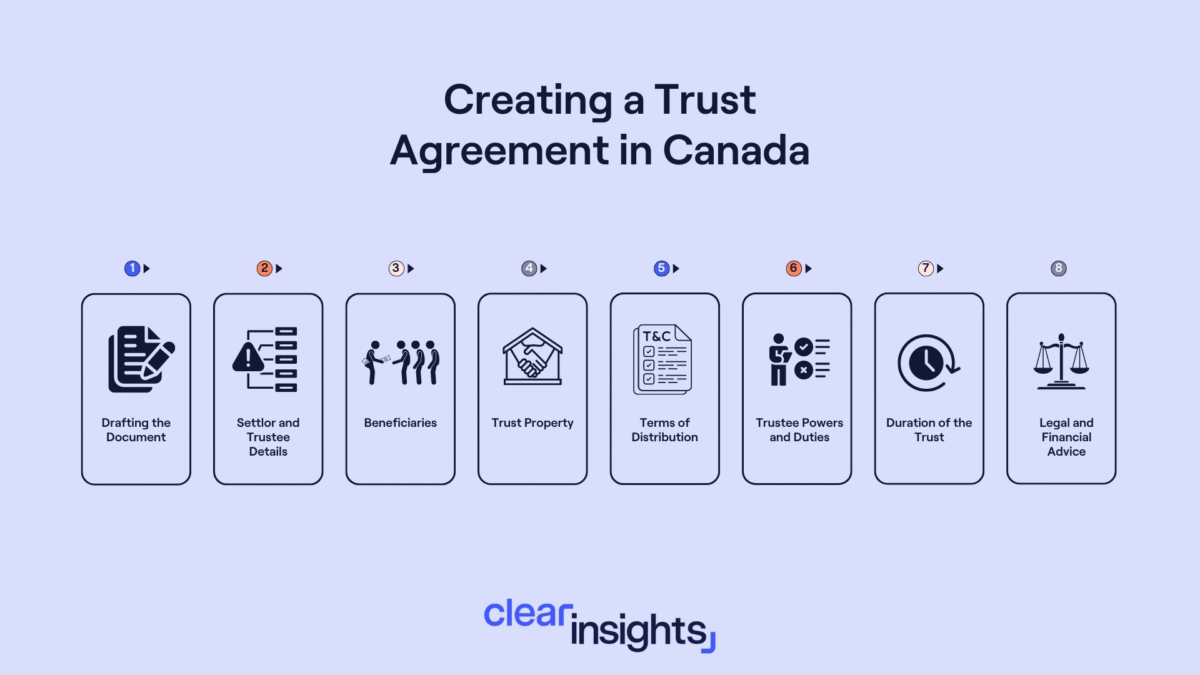
Creating a family trust in Canada in 2025 requires careful planning, legal compliance, and a clear understanding of your estate goals. Whether you're looking to protect your wealth, minimize taxes, or ensure a smooth transfer of assets, setting up a trust involves several key steps. Working with estate planning experts and legal professionals will help you structure the trust correctly and maximize its benefits. Below is a step-by-step breakdown of the process to establish a legally valid family trust.
Define Your Objectives: Clearly determine the purpose of the trust, including how assets will be managed, protected, and distributed. Identifying your objectives ensures you choose the appropriate trust type—inter-vivos, testamentary, revocable, or irrevocable—to align with your financial and estate planning needs.
Select the Right Trustee and Beneficiaries: Choose a trustworthy trustee who will oversee the trust. Define their responsibilities and tasks in detail.,Clearly identify the beneficiaries and specify the assets they are to receive.
Draft the Trust Agreement with Legal Help: Collaborate with an estate planning attorney or tax lawyer to draft a comprehensive trust agreement. This legal document should lay out the trust’s purpose, name the trustees and beneficiaries, and include clauses specific to asset management and distribution.
Fund the Trust: Make an initial contribution to the trust, which can be a nominal amount like a small sum of money or a symbolic item such as a silver coin.
Establish a Trust Bank Account: Open a bank account in the name of the trust to manage the trust’s finances effectively.
Asset Transfer: Transfer the designated assets into the trust. This may include a wide range of valuables such as real estate, vehicles, investments, and bank accounts.
Legal Formalities: Depending on your province, registration may be required to meet 2025 regulatory updates and ensure compliance with Canadian trust laws.
Finalize the Process: Implement a closing agenda with your tax practitioner to ensure all assets are transferred correctly and all legal formalities are completed.
Choosing the right trustee requires assessing financial skills, reliability, and fairness. Beneficiaries should align with the trust’s purpose and be clearly designated.
The roles and responsibilities of trustees are to invest, manage, and distribute the trust’s assets. They must also perform administrative duties to ensure trust expenses and fees are paid. Beneficiaries receive and enjoy the assets according to the standards and methods laid out in the trust. They have the right to capital and income distribution as outlined in the trust document and have equitable title to the trust’s property.
Even though trusts are not separate legal entities, they are treated as a separate taxpayer, and you must file a T3 tax return, report its own income, and pay the income tax bill. Let’s consider the various tax implications:
In 2025, the top marginal tax rate for an individual starts after $609,359, while that of trusts is $15,200. Canadian trusts reach the highest marginal income tax rate at an extremely lower threshold than individual taxpayers. The inter-vivos marginal tax rate is 33% nationally, but the provincial rate varies between 15% and 25%. Testamentary trusts generally benefit from graduated tax rates if they qualify as a Graduated Rate Estate (GRE) or Qualified Disability Trust (QDT). Otherwise, they are taxed at the top marginal rate.
The income the trust receives comes from diverse sources of revenue, such as capital gains, dividends, and business income. The taxable income is then calculated by subtracting this income from the deductions and credits made to the trust. After the calculations, use the taxable income rate (currently at 33%) to calculate the taxes payable - testamentary trusts may benefit from lower rates if they qualify as GREs.
A family trust allows income splitting, where the trust’s income is distributed to the beneficiaries in a lower income bracket than the settlor. This provision minimizes the amount of tax payable. On capital gains, the trust can allocate the capital gain to the beneficiaries with lower marginal tax rates. Further, the trust allows deferment of capital gain taxes until the beneficiaries decide to sell the assets. This provision can help the beneficiary plan for taxes and minimize the tax burden.
A family trust with shares in a Canadian corporation can benefit from the dividend tax credit. When your family trust becomes eligible for dividends, you can claim the dividend tax credit and reduce the amount you pay as tax for the dividend income. The dividend tax credit is among the tax benefits because it prevents double taxation on corporate profits as it appreciates that the corporation had already paid income tax before distribution.
In Canada, the 21-year rule in family trusts under the Income Tax Act considers that a family trust disposes of the property 21 years from the date it was created. This rule means that the trust is assumed to have sold the assets, and the capital gains are subject to taxation. NOTE: Planning for the 21-year rule should begin well in advance and consider various legal and tax implications.
The main aim of this rule is to prevent indefinite deferral of capital gains tax on property held within a trust. The trust can continue after the 21-year mark, with subsequent deemed dispositions every 21 years thereafter. A trustee can prevent excessive loss of assets from capital gains tax by:
Family trusts are a preferred estate planning tool due to their unique advantages in asset protection, tax efficiency, and control over wealth distribution.. Here are three undeniable benefits:
Asset protection: When you transfer your assets to a family trust (discretionary), you protect it from lawsuits, creditors, and other unforeseeable claims. Since you transferred the asset to the trust, it does not belong to you or the beneficiaries. Once assets are placed in a discretionary family trust, they are shielded from legal claims, creditor demands, and financial liabilities.
Tax advantages: One of the primary tax advantages of a family trust is reducing estate tax liability, particularly for high-net-worth individuals. Canada doesn't have an estate tax, but family trusts can help reduce probate fees and income taxes at death. Trusts also allow income splitting with limited income splitting opportunities. This is where taxation is distributed to the beneficiaries, and those falling within a lower income bracket than you will receive the benefits at a reduced tax rate.
Control over assets: Although you may lose ownership of the assets after you create the trust agreement, you can maintain control by choosing a trustworthy trustee. You must also ensure you created a detailed trust document stating how everything should be done and the precise role of beneficiaries.
For a detailed walkthrough, explore our expert guide on transferring real estate into a family trust."
As an estate planning tool, a family trust secures your loved ones’ future and helps you minimize your tax liability, protect your assets, and avoid probate. Choosing a trustworthy and reliable trustee ensures you acquire superior asset management services before and after your demise.
Careful financial planning can help reduce the tax implications and allow you to enjoy the various tax benefits. As a settlor creates the trust, they must be aware of the 21-year rule in Canada and plan for it with the assistance of an estate planning expert. Book a free consultation with us, and let us help you safeguard your future.
 Secure Your Legacy
Secure Your Legacy
Get your free 12-step Estate Planning checklist now. 89% of readers complete their estate plan within 3 months of using our guide.
Instantly Access Now